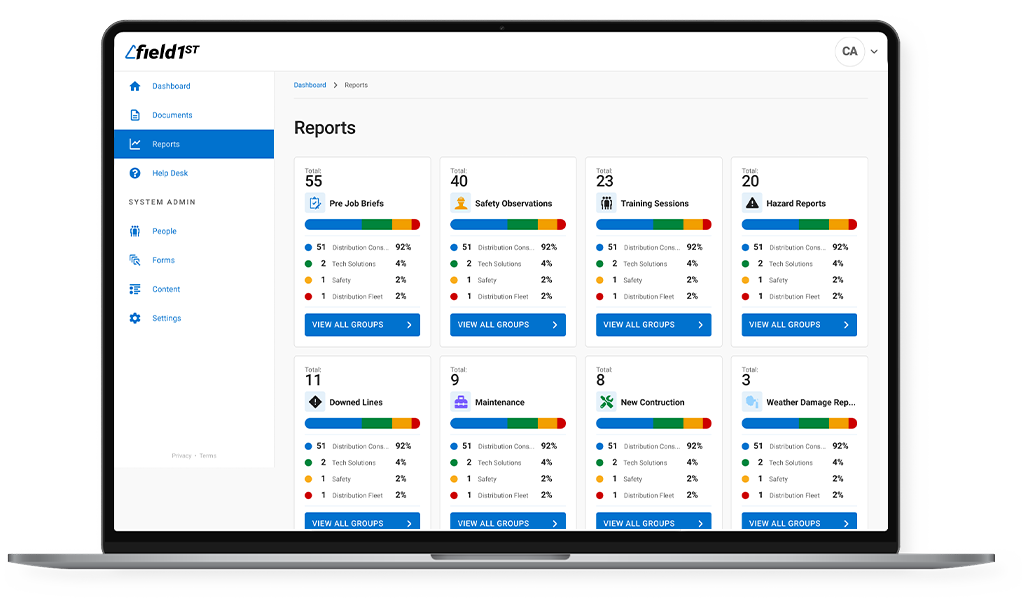
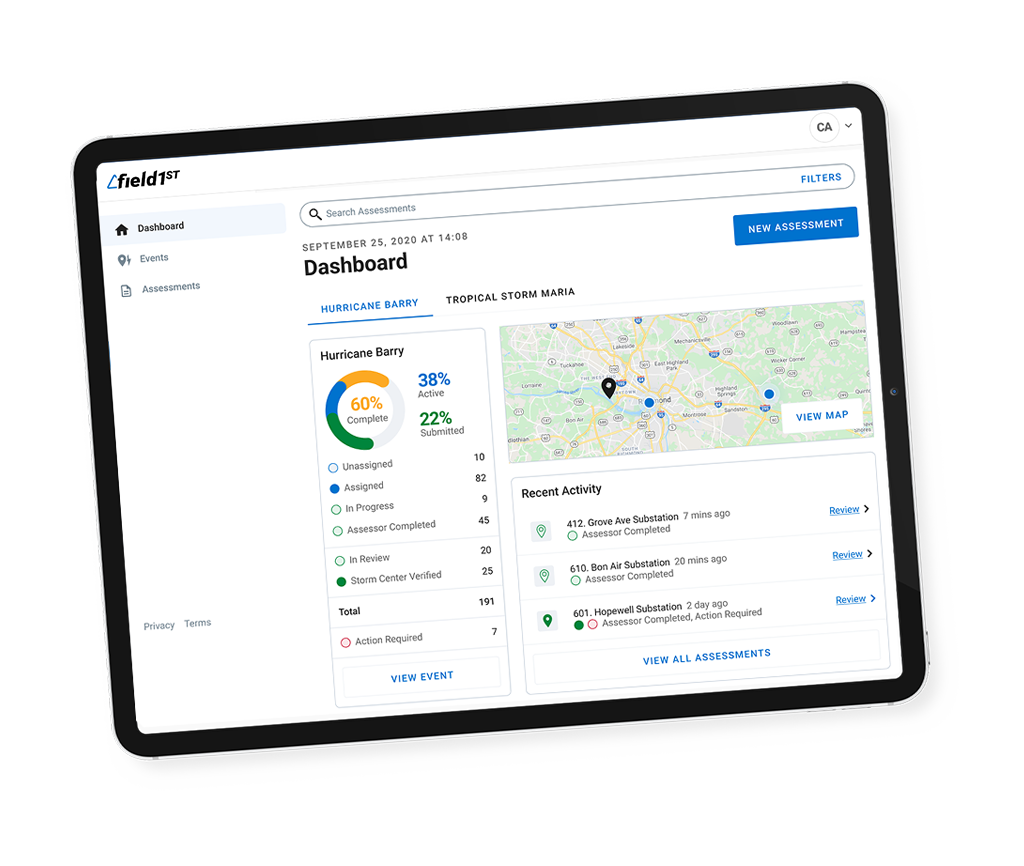
Hazcom training is a critical aspect of workplace safety that ensures employees have the knowledge and understanding of the hazards associated with the chemicals they may come into contact with while on the job. It is a key component of OSHA’s hazard communication standard, also known as HazCom. Compliance with HazCom requirements is not only necessary for legal reasons but also for the well-being of employees and the overall success of a business. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the best practices for mastering HazCom training, providing a safer workplace for everyone.
Why Hazcom Training Matters
Effective HazCom training is vital because it empowers employees with the necessary information to protect themselves from hazardous chemicals in the workplace. By understanding the risks associated with these chemicals, employees can take appropriate precautions and follow proper safety protocols. HazCom training also promotes a culture of transparency and collaboration, as employees are encouraged to communicate any concerns or incidents related to hazardous chemicals.
The consequences of inadequate HazCom training can be severe. Not only does it put employees at risk of injury or illness, but it can also result in OSHA violations and fines for non-compliance. Furthermore, failure to provide proper HazCom training can lead to low employee morale, high turnover rates, and damage to a company’s reputation. To ensure a safe and compliant workplace, organizations must prioritize HazCom training and implement best practices to effectively deliver this important information to their employees.
Identifying Hazcom Training Needs
Before implementing a HazCom training program, it is crucial to identify which employees require training. HazCom training should be provided to all employees who may be exposed to hazardous chemicals in their work environment. According to OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard (HCS), any chemical that is present in the workplace in a manner that employees may be exposed to under normal conditions or in foreseeable emergencies falls under the scope of HazCom training.
To determine which employees need training, organizations must conduct a thorough assessment of their workplace and job tasks. This assessment should consider the chemicals used, potential routes of exposure, and the likelihood of accidents or equipment failures that could result in uncontrolled chemical releases. Consulting employees and involving them in the decision-making process can provide valuable insights into potential hazards and improve the overall effectiveness of the training program.
Building a Comprehensive Hazcom Training Program
A well-designed HazCom training program is essential for effectively communicating information about hazardous chemicals to employees. It should cover all the necessary elements to ensure compliance with OSHA requirements and promote a safe working environment. Here are the key steps to building a comprehensive HazCom training program:
Step 1: Assess Training Needs
Start by conducting a thorough assessment of the training needs within your organization. This assessment should consider the specific hazards present, the job tasks performed by employees, and any regulatory requirements that must be met. By understanding the specific training needs, you can tailor the program to address the unique risks and challenges faced by your workforce.
Step 2: Develop a Written Training Plan
A written training plan serves as a roadmap for your HazCom training program. It outlines the objectives, content, and delivery methods for the training. The plan should include details on the training materials, trainers, and evaluation methods to ensure the effectiveness of the program. It should also specify the frequency of training and any refresher courses that may be required.
Step 3: Create Engaging Training Materials
Developing engaging and interactive training materials is essential for capturing employees’ attention and facilitating their understanding of the subject matter. Consider using a variety of training methods, such as presentations, videos, quizzes, and hands-on demonstrations. Incorporate real-life examples and case studies to make the training relevant to employees’ work experiences.
Step 4: Tailor Training to Job Roles
Different job roles may have different levels of exposure to hazardous chemicals. Tailor the training content to address the specific needs and responsibilities of each job role. For example, employees who handle chemicals directly may require more in-depth training than those who have limited contact with chemicals.
Step 5: Provide Training in Multiple Formats
People learn in different ways, so it is important to provide training in multiple formats to accommodate various learning styles. Offer in-person training sessions, online courses, and printed materials to ensure that all employees have access to the training in a format that suits them best. Consider translating the training materials into different languages if necessary to accommodate a diverse workforce.
Step 6: Incorporate Ongoing Training and Refreshers
HazCom training is not a one-time event. It should be an ongoing process to ensure that employees stay up to date with the latest information and best practices. Incorporate regular refresher training sessions to reinforce key concepts and address any updates or changes in regulations. Encourage employees to ask questions and provide feedback to foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
Hazcom Training Best Practices
To enhance the effectiveness of your HazCom training program, consider implementing the following best practices:
1. Use Clear and Accessible Communication
HazCom training materials should use clear and concise language that is easy for employees to understand. Avoid technical jargon and use visuals, diagrams, and examples to illustrate important concepts. Make sure that the training materials are accessible to all employees, including those with disabilities or language barriers. Provide translations or interpreters as needed to ensure that everyone can fully participate in the training.
2. Emphasize the Importance of Hazard Communication
During training, emphasize the importance of hazard communication and its role in promoting a safe workplace. Help employees understand that hazard communication is not just a compliance requirement but a crucial element of their own safety and the safety of their colleagues. Highlight real-life examples of incidents that could have been prevented through effective hazard communication to underscore the relevance and importance of the training.
3. Encourage Active Participation
Engage employees in the training process by encouraging active participation. Incorporate interactive elements such as group discussions, case studies, and hands-on activities to foster engagement and promote knowledge retention. Encourage employees to ask questions, share their experiences, and contribute to the discussion. This participatory approach creates a collaborative learning environment and helps employees internalize the training material.
4. Provide Real-Life Scenarios and Examples
Make the training content relatable by providing real-life scenarios and examples that employees can connect with. Use case studies or stories to illustrate the consequences of inadequate hazard communication and the benefits of effective communication. This approach helps employees understand the practical implications of the training and encourages them to apply the knowledge in their day-to-day work.
5. Incorporate Hands-On Training
Whenever possible, incorporate hands-on training to allow employees to apply their knowledge in a practical setting. Provide opportunities for employees to handle and work with simulated hazardous chemicals under controlled conditions. This hands-on experience reinforces the training concepts and helps employees develop the necessary skills and confidence to handle hazardous chemicals safely.
6. Evaluate and Measure Training Effectiveness
Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of your HazCom training program to ensure its ongoing improvement. Use surveys, quizzes, and assessments to gather feedback from employees and assess their understanding of the training material. Analyze training metrics, such as completion rates and performance indicators, to identify areas for improvement. Use this feedback to refine your training program and address any gaps or challenges.
Your Safety, Our Priority
Ensuring worker safety near power lines is a complex but crucial task. By adhering to OSHA guidelines and implementing robust safety measures, companies can significantly reduce the risks involved.
Choose Field1st for Proactive Safety
Field1st offers an all-encompassing solution designed to help you effortlessly comply with OSHA guidelines. Our platform enables real-time monitoring and proactive safety measures, ensuring that you are always ahead of the curve when it comes to maintaining a safe work environment. Don’t leave safety to chance; choose Field1st for a proactive, comprehensive approach to worker safety.
Contact us today to discover how Field1st can simplify OSHA compliance and elevate your commitment to worker safety.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What Is Hazcom Training and Why Is It Important?
Answer: Hazcom Training, or Hazard Communication Training, educates employees about the hazards of chemicals and substances they may encounter in the workplace. It’s crucial for ensuring a safe work environment and is mandated by OSHA.
2. What Are the Key Elements of Effective Hazcom Training?
Answer: Effective Hazcom Training should include information on how to read Safety Data Sheets (SDS), proper labeling of chemicals, and emergency response procedures for chemical exposures.
3. How Often Should Hazcom Training Be Conducted?
Answer: OSHA recommends that Hazcom Training be conducted at the time of an employee’s initial assignment and whenever a new chemical hazard is introduced into their work area.
4. What Are Some Best Practices for Hazcom Training?
Answer: Best practices include interactive training sessions, regular updates on new chemical hazards, and practical demonstrations on how to handle emergencies.
5. How Can I Make Hazcom Training More Engaging for Employees?
Answer: Use a mix of training methods like videos, quizzes, and hands-on demonstrations to keep the training engaging. Real-life case studies can also make the training more relatable.
6. Is Online Hazcom Training Effective?
Answer: Online Hazcom Training can be effective if it’s interactive, up-to-date, and followed by practical assessments. However, it should be supplemented with in-person training for best results.
7. How Do I Know If My Hazcom Training Is Effective?
Answer: Regular assessments, employee feedback, and monitoring workplace incidents related to chemical hazards are good indicators of the effectiveness of your Hazcom Training.
8. Are There Any Tools to Help Manage Hazcom Training?
Answer: Yes, there are specialized training management systems that can help you schedule, track, and assess the effectiveness of your Hazcom Training programs.
9. What Are the Legal Requirements for Hazcom Training?
Answer: Hazcom Training is mandated by OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard (HCS), which requires employers to provide information and training on hazardous chemicals in a manner employees can understand.
10. How Can Hazcom Training Improve Overall Workplace Safety?
Answer: By educating employees on the safe handling of hazardous chemicals, Hazcom Training helps prevent accidents, reduces health risks, and fosters a culture of safety in the workplace.