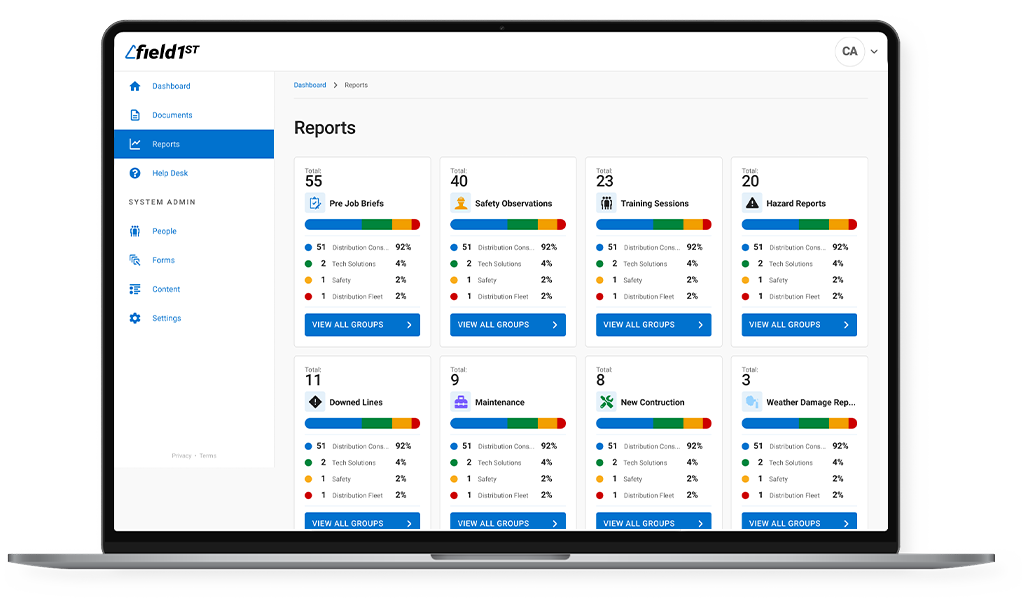
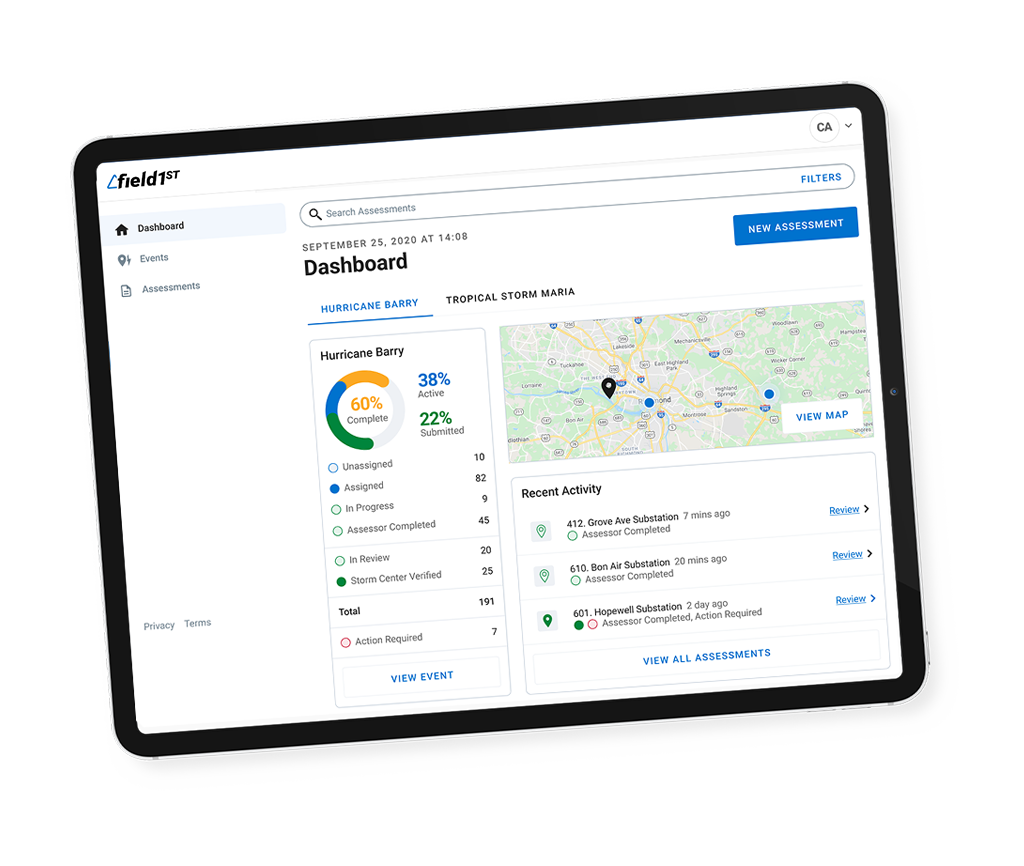
The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a game-changer in contemporary workplace safety. The International Labor Organization estimates that over 2.8 million workers lose their lives to occupational illnesses or accidents each year. This is an overwhelming figure that affects almost every employee and all aspects of the business. By harnessing the power of IoT devices, organizations can now revolutionize their safety protocols and create secure work environments for employees.
IoT devices play a crucial role in monitoring and alerting workplace safety by providing real-time data collection, analysis, and communication capabilities. These devices are embedded with sensors and connected to the internet, allowing them to gather information from the environment and transmit it to a central system for analysis.
In this article, we explore the pivotal role played by IoT devices in monitoring and alerting for workplace safety, shedding light on their potential to minimize internal and external risks and enhance overall safety measures.
What are IoT Devices?
IoT devices, also known as the Internet of Things devices, are physical objects such as sensors, gadgets, and machines that connect wirelessly to a network and have the ability to share data with other devices and systems and provide critical services to users. These actuators, which can vary from simple sensors to large machinery and appliances, are increasingly being utilized in a variety of industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, supply chain management, and transportation sectors to provide real-time insights and facilitate managerial decision-making.
Workplace Safety is Critical for Business Success
Workplace safety is a vital component of business operations at any firm. According to a report by the European Agency for Safety and Health at Work, approximately 150 million working days are lost every year as a result of work-related accidents. Providing a safe workplace not only saves employees from injuries and accidents, but also helps ensure their overall well-being and job satisfaction.
Employers are responsible for identifying possible risks and hazards in the workplace and taking the appropriate precautions to prevent accidents. A safe workplace is also beneficial to productivity and efficiency. Employees are more likely to focus on their duties and responsibilities and perform well when they feel safe in their workplace. Furthermore, addressing and mitigating risks can assist businesses in avoiding costly legal action and compensation claims.
Employers can lower the likelihood of accidents and protect themselves from any legal liability by establishing safety standards, observing best practices, and providing proper safety training to their staff members.
How is IoT Leading to a Safer Workplace?
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in workplace safety has far-reaching implications for understanding the various risks and hazards that may be present, diagnosing potential dangers, and designing solutions that are both practical and scalable.
IoT gadgets, such as environmental sensors, equipment monitoring devices, smart cameras, and IoT-enabled wearables, are often used to improve worker safety and reduce possible risks and dangers. These gadgets and equipment can be used to monitor workplace variables such as temperature, humidity, air quality, and noise levels, as well as workers’ physical metrics like heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature.
They are also increasingly being used to track the position of personnel and equipment in real time, as well as detect probable safety issues. The implementation of IoT devices in workplace safety has the potential to minimize the number of workplace accidents and injuries while boosting overall safety and productivity.
The Growing Role of IoT Devices in Workplace Safety
The role of IoT devices in workplace safety is rapidly growing due to advancements in technology and increased awareness of the importance of creating safe work environments. IoT devices offer several benefits that contribute to improving workplace safety, including real-time monitoring, proactive hazard detection, remote monitoring and control, and data-driven decision-making.
There are many types of IoT devices used in workplace safety to monitor and enhance safety protocols. These range from wearables to smart home gadgets to industrial sensors and video surveillance cameras. These gadgets are used to gauge a wide range of metrics, including environmental monitoring, location tracking, performance measurement, and device control.
IoT devices are able to share valuable insights and data in real time and provide remote management and control because of their interoperability and capacity to communicate with one another and with cloud-based systems. The enhanced productivity, efficiency, and convenience that IoT devices provide could be advantageous to a wide range of industries and applications.
It is then reasonable to anticipate that in the not-too-distant future, IoT devices will be put to even more creative and consequential uses, and strengthen our existing safety control frameworks and emergency response systems.
Commonly Used IoT Devices for Workplace Safety
There are many types of IoT devices for workplace safety that organizations employ to enhance safety measures and protect employees. The following are some common Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices used to keep employees safe at work.
1. Smart Surveillance Cameras
IoT-enabled smart surveillance cameras allow for real-time monitoring of the workplace. These cameras are capable of detecting unwanted entry, monitoring staff activity, and identifying possible safety violations.
2. Wearable Devices
Wearable devices equipped with IoT sensors, such as smart helmets or safety vests, can help monitor vital signs, detect falls, and give prompt aid during crises. They also enable firms to track employees’ whereabouts and well-being in dangerous locations and situations.
3. Environmental Sensors
Internet of Things-enabled environmental sensors can monitor air quality, temperature, humidity, vibrations, carbon monoxide levels, and weather changes. These sensors give early alerts of possible risks, such as gas leaks or fires, allowing for preemptive action.
Benefits of Using IoT Devices for Workplace Safety
The adoption of IoT devices for workplace safety offers numerous benefits, including:
- Real-time monitoring and data collection for identifying potential hazards promptly
- Proactive alerting systems that notify employees and management about potential dangers
- Enhanced emergency response times through immediate alerts and location tracking
- Integration with existing safety measures to augment existing safety protocols
- Improved compliance with safety standards and industry regulations
- Reduction in workplace accidents, injuries, and associated costs
How IoT Devices Enable Real-time Monitoring
IoT devices enable real-time monitoring by leveraging their interconnectedness and data transmission capabilities. The sensors embedded in these devices capture vital information, such as environmental conditions, employee movements, and equipment performance. This data is then transmitted and analyzed instantaneously, providing organizations with actionable insights to maintain a safe work environment.
Data Collection and Analysis for Identifying Potential Hazards
The data collected by IoT devices is invaluable for identifying potential hazards. Advanced analytics tools can process this data and generate meaningful reports and visualizations, highlighting patterns, trends, and anomalies. By analyzing this information, organizations can proactively address safety concerns, implement preventive measures, and ensure the well-being of their workforce.
Proactive Alerting Systems
Proactive alerting systems are designed to detect and notify potential dangers before they escalate into emergencies. By leveraging IoT devices, organizations can establish robust alerting systems that trigger immediate responses and mitigate various risks effectively.
The Role of IoT Devices in Detecting and Notifying Potential Dangers
IoT devices can help detect abnormal conditions or activities that pose safety risks to employees. These devices can send real-time alerts to staff members, supervisors, and emergency response teams, ensuring swift action is taken to prevent accidents or mitigate their negative impact. Here are some key ways in which IoT devices contribute to detecting and notifying potential dangers in the workplace:
Environmental Monitoring: As already mentioned. IoT devices can monitor environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, air quality, and noise levels. By continuously collecting data from these sensors, the devices can detect hazardous conditions like excessive heat, poor air quality, or high noise levels that may impact employee safety and well-being.
Hazardous Gas Detection: IoT-enabled gas sensors can detect the presence of harmful gasses or volatile compounds in the workplace. These sensors can continuously monitor gas levels and send real-time alerts when dangerous concentrations are detected. This early detection allows employees to evacuate the area quickly and take necessary precautions.
Fire Detection and Prevention: IoT devices integrated with fire alarms and smoke detectors can quickly identify signs of fire, smoke, or increased temperature. When a potential fire hazard is detected, the IoT devices can immediately send alerts to emergency response personnel, allowing for swift action to be taken to extinguish the fire and evacuate the premises if necessary.
Equipment Monitoring: IoT devices can be used to monitor the performance and condition of equipment and machinery used in the workplace. By collecting data on parameters such as temperature, vibration, or energy consumption, IoT devices can detect abnormalities or signs of equipment malfunction. These devices can then send alerts to maintenance personnel or supervisors, enabling timely maintenance or repair to prevent potential accidents or equipment failures.
Motion and Fall Detection: Wearable IoT devices equipped with motion sensors can monitor employees’ movements and detect falls or accidents. If an employee falls or experiences a sudden impact, the device can automatically send an alert to designated personnel, ensuring prompt assistance is provided.
Video Surveillance and Intrusion Detection: IoT-enabled cameras and sensors can be used for video surveillance and intrusion detection in workplaces. These devices can monitor restricted areas, detect unauthorized access, and raise alarms in case of suspicious activities or security breaches.
How IoT Devices Can Complement and Enhance Traditional Safety Protocols
With the ability to connect and communicate through sensors, devices, and systems, IoT has brought about significant advancements in ensuring a safe working environment. Here are some examples:
1. The Role of Safety Inspections
IoT devices enhance safety inspections by providing real-time data on equipment conditions, environmental factors, and potential hazards. Sensors can detect abnormalities, monitor critical parameters, and alert safety personnel to take prompt preventive measures.
2. Awareness and Continuous Improvement
IoT systems enable the collection of vast amounts of data related to safety incidents, near-misses, and employee behavior. By analyzing this data, organizations can identify patterns, root causes, and trends, leading to informed decisions and continuous safety improvements.
3. Digital Transformation in Safety Management
The implementation of IoT frameworks facilitates digital transformation in safety management by automating processes, streamlining workflows, and integrating safety systems. This ensures timely incident reporting, quick response to emergencies, and improved overall safety performance.
4. The Importance of Knowledge Sharing
IoT devices allow for seamless knowledge sharing by providing a centralized platform where safety-related information can be accessed and shared across the organization. This helps in disseminating best practices and safety protocols to enhance awareness and promote a safety-first culture.
5. Real-time Transparency and Visibility
IoT-enabled devices offer real-time transparency and visibility into safety-related data, such as equipment status, worker locations, and environmental conditions. This enables immediate identification of potential risks and hazards, allowing for prompt corrective actions to be taken.
6. Digitizing Operations
IoT devices help in digitizing and automating safety operations by capturing and analyzing data in real-time. This data can be used to optimize daily operations and routine processes, predict safety incidents, and allocate resources accordingly. By digitizing operations, organizations can proactively manage safety risks and minimize the likelihood of accidents.
7. Enabling Predictive Maintenance
Traditional safety protocols often involve routine maintenance schedules based on time intervals or predetermined criteria. However, these schedules may not account for actual equipment usage or the real-time condition of the machinery. IoT devices can monitor equipment performance metrics, such as vibration, temperature, or energy usage in real-time.
By analyzing this data, IoT devices can detect signs of potential failures or malfunctions before they occur. This enables proactive maintenance actions to be taken, thus, reducing the risk of unexpected equipment downtime, accidents, or production interruptions.
Emerging Technologies in IoT Devices for Workplace Safety
The field of IoT devices for workplace safety is continuously evolving. Some emerging technologies that hold promise for the future include:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing business operations in many industries across the world. In workplace safety too, AI algorithms can enhance the capabilities of IoT devices by enabling advanced pattern recognition, predictive analytics, and anomaly detection.
Edge Computing: By processing data locally on IoT devices rather than relying on cloud-based processing, edge computing reduces latency and improves real-time response capabilities.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies can provide immersive training experiences, simulating hazardous scenarios and improving safety awareness and preparedness.
The Future of IoT Devices in Monitoring and Alerting for Workplace Safety
The implementation of IoT-enabled safety systems can contribute to a positive work culture and employee engagement. When employees feel that their safety is prioritized, it fosters a sense of trust and confidence in the organization. This, in turn, leads to increased job satisfaction, productivity, and retention rates.
As we look to the future, the potential of IoT devices in workplace safety monitoring and alerting is, no doubt, promising. With continued advancements in technology, we can expect to see further innovation in sensor capabilities, connectivity, and data analytics. These developments will establish a new standard for workplace safety, creating safer and more secure working environments while simultaneously supporting the well-being and job satisfaction of employees.
Leverage the Power of IoT
Businesses frequently face financial and non-financial losses due to accidents at the workplace. By leveraging the power of IoT, organizations can create safer work environments, mitigate risks, and protect their most valuable asset—their employees. It is essential for today’s businesses to embrace this technology and integrate IoT devices with existing safety measures to achieve comprehensive and effective workplace safety.
In these dynamic times, staying updated with the latest advancements and trends in workplace safety is critical for business success. By leveraging the power of IoT devices, organizations can unlock new levels of safety, efficiency, and productivity. Let us embrace this transformative technology and create a safer future for all!
Take advantage of an enterprise platform focused on reducing OSHA-reported incidents through onsite pre-job briefings, safety observation monitoring, and reporting tailored to your industry. Reach out to learn more about Field1st or to request a demonstration.